Sevalla
In this tutorial, you will learn how to prepare and deploy a Ktor application to Sevalla. You can use one of the following initial projects, depending on the way used to create a Ktor server:
Prerequisites
Before starting this tutorial, you need to create a Sevalla account (comes with $50 in free credits).
Clone a sample application
To open a sample application, follow the steps below:
Clone the Ktor documentation repository.
Open the codeSnippets project.
Open the embedded-server or engine-main sample, which demonstrates two different approaches to setting up a Ktor server — either by configuring it directly in code or through an external configuration file. The only difference in deploying these projects is how to specify a port used to listen for incoming requests.
Prepare the application
Step 1: Configure the port
Sevalla injects a random port using the PORT environment variable. Your application must be configured to listen on that port.
If you've chosen the embedded-server sample with server configuration specified in code, you can obtain the environment variable value using System.getenv(). Open the Application.kt file placed in the src/main/kotlin/com/example folder and change the port parameter value of the embeddedServer() function as shown below:
If you've chosen the engine-main sample with server configuration specified in the application.conf file, you can assign the environment variable to the port parameter by using the ${ENV} syntax. Open the application.conf file placed in src/main/resources and update it as shown below:
Step 2: Add a Dockerfile
To build and run your Ktor project on Sevalla, you need a Dockerfile. Here’s a sample Dockerfile using a multi-stage build:
Make sure to replace <project-name> with the project name defined in your settings.gradle.kts file:
Deploy the application
Sevalla builds and deploys your application directly from a connected Git repository. This can be hosted on platforms like GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, or any supported Git provider. To deploy successfully, ensure your project is committed and pushed, and includes all necessary files (such as your Dockerfile, build.gradle.kts, and source code).
To deploy the application, sign in to Sevalla and follow the steps below:
Click Applications -> Create an app
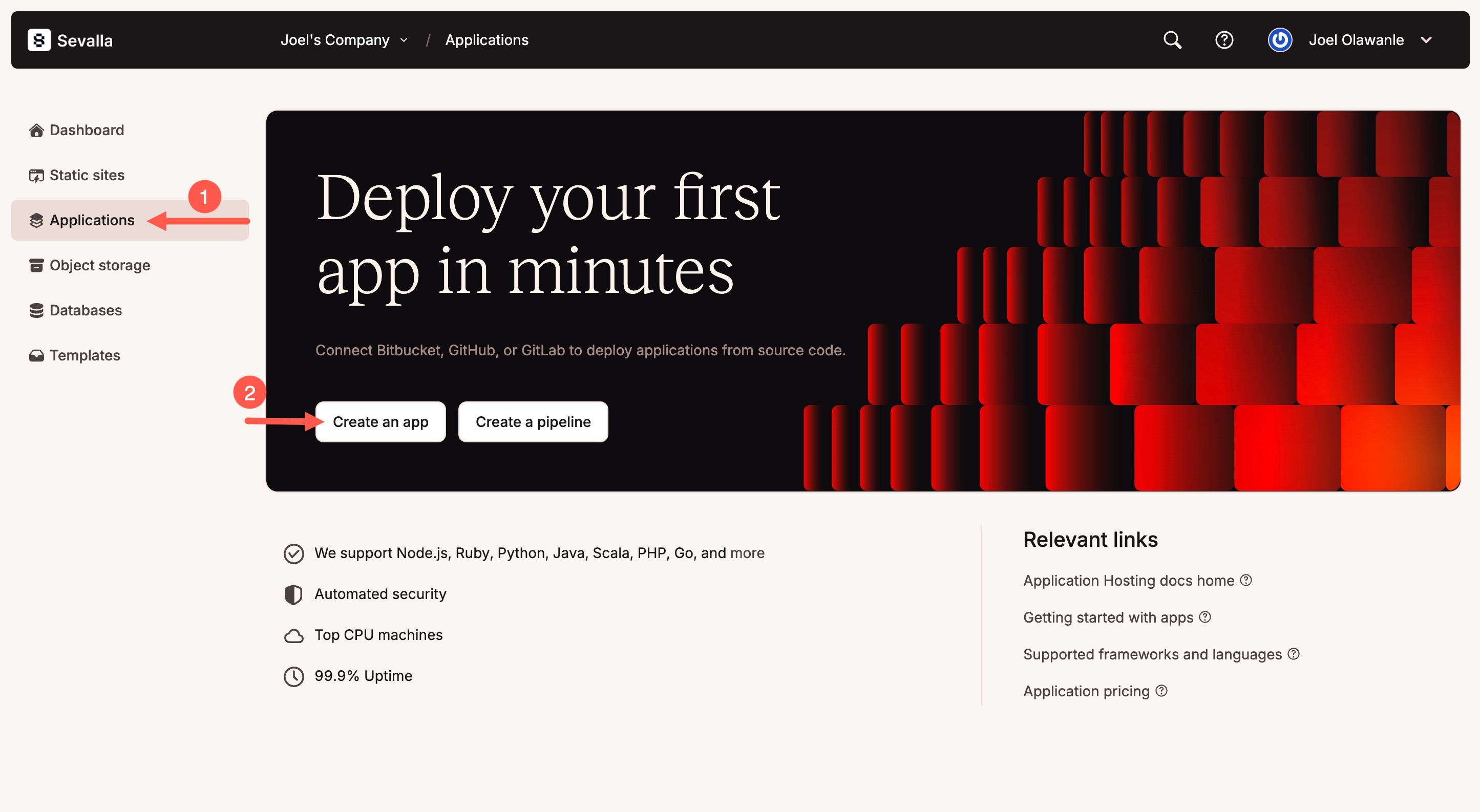
Choose your Git repository and select the appropriate branch (usually
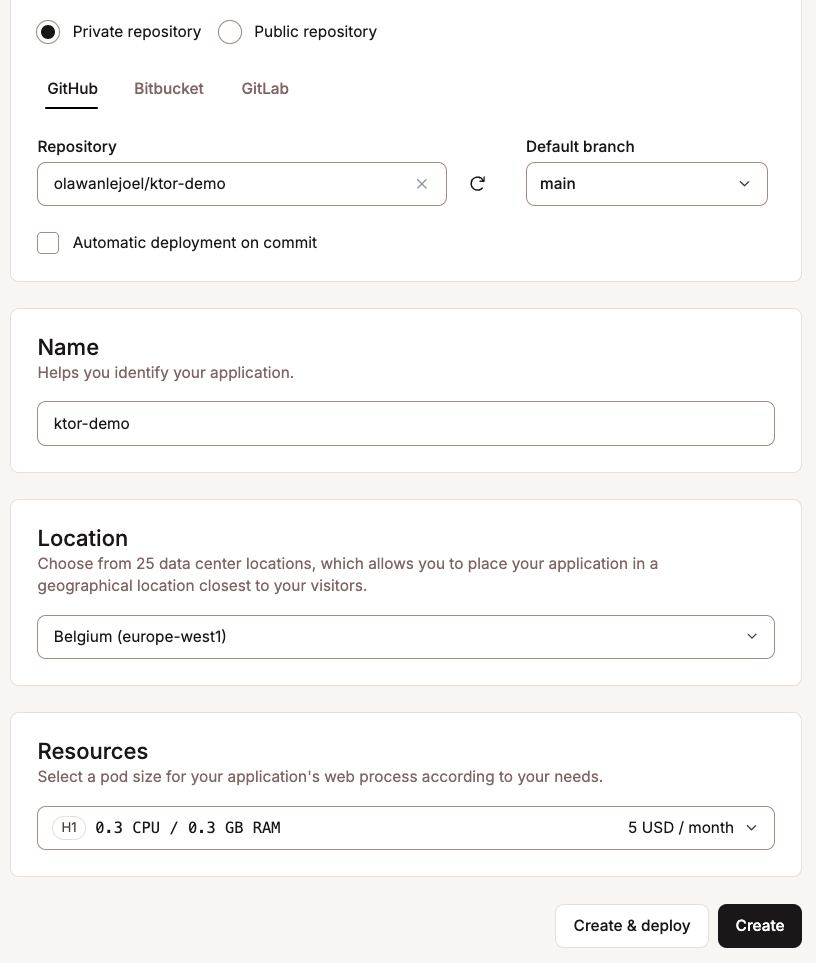
mainormaster).Set the application name, select a region, and choose your pod size (you can start with 0.5 CPU / 1GB RAM).
Click Create, but skip the deploy step for now
Go to Settings -> Build and click Update Settings under the Build environment card.
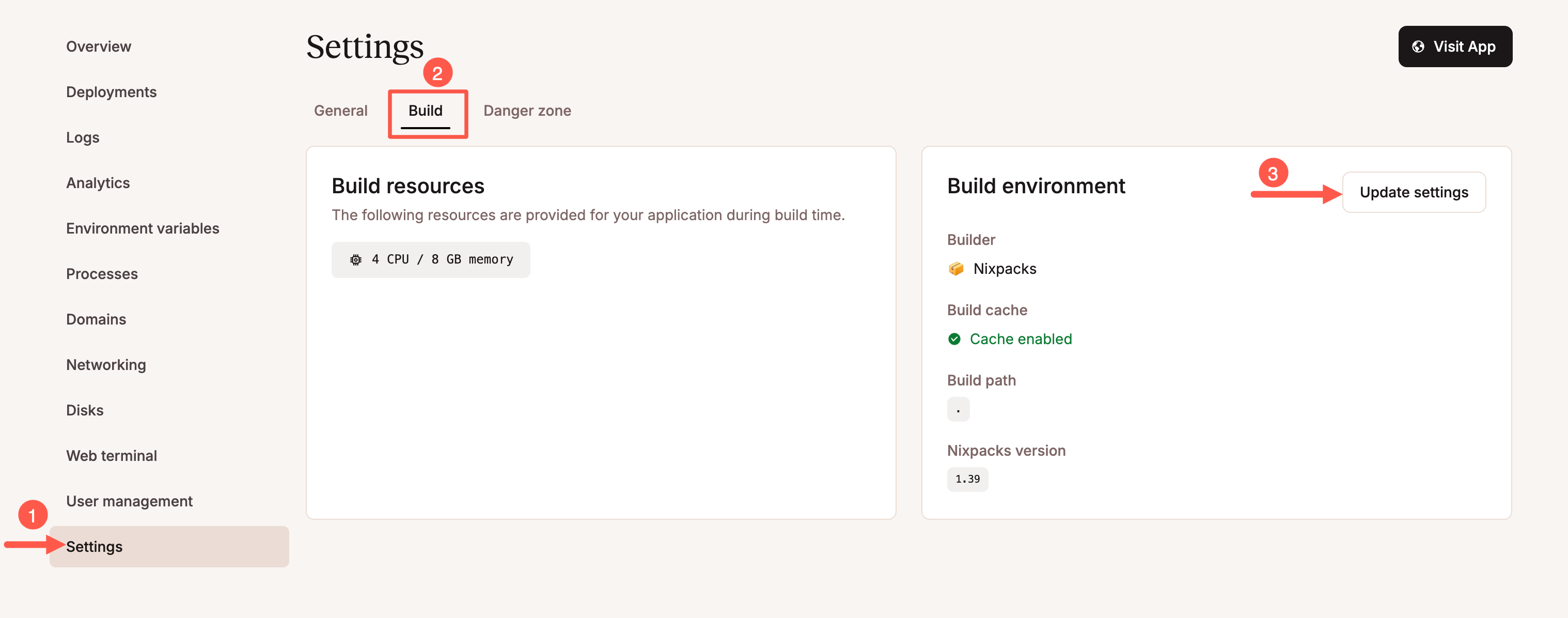
Set the build method to Dockerfile.
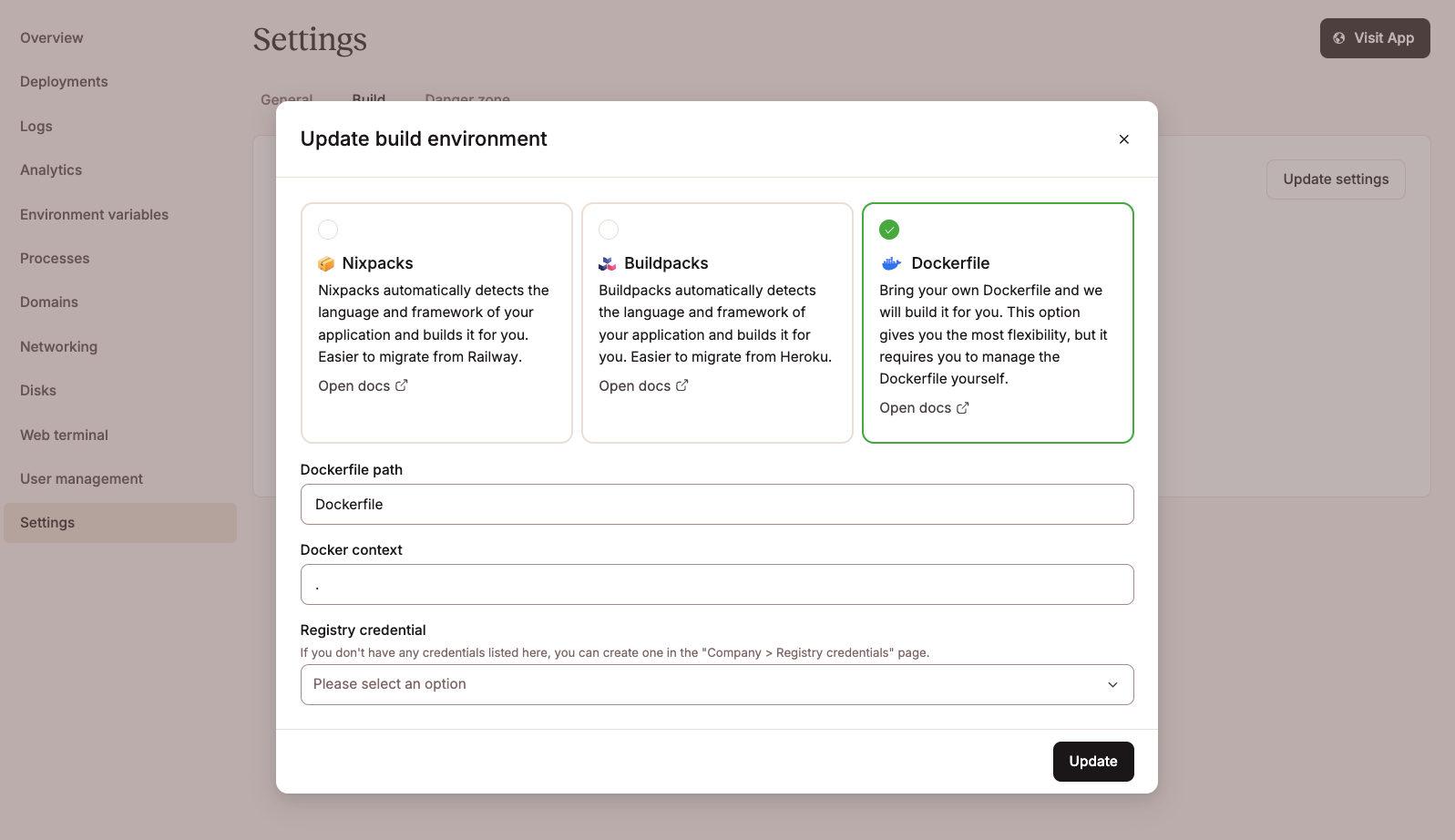
Confirm the Dockerfile path is
Dockerfileand the Context is..Return to your application's Deployment tab and click Deploy.
Sevalla will clone your Git repository, build the Docker image using your Dockerfile, inject the PORT environment variable, and run your application. If everything is configured correctly, your Ktor app will be live at https://<your-app>.sevalla.app.